हा लेख CTET-2026 – Water (Geography) या विषयावर आधारित असून मराठी + इंग्रजी मिश्र भाषेत सोप्या व परीक्षाभिमुख पद्धतीने मांडलेला आहे. या लेखामध्ये पाण्याचे महत्त्व, पृथ्वीवरील पाण्याचे वितरण, जलचक्र, पाण्याचे स्रोत, नद्यांचे महत्त्व, पाण्याचे उपयोग, पाणीटंचाई, पाण्याचे प्रदूषण, पाणी संवर्धन तसेच भारतातील जल व्यवस्थापन या सर्व महत्त्वाच्या घटकांची सविस्तर माहिती देण्यात आली आहे. CTET Paper-I आणि Paper-II साठी उपयुक्त असलेला हा लेख EVS व Geography विषयाच्या अभ्यासासाठी मदत करणारा असून, संकल्पना स्पष्ट करण्यासाठी सोप्या शब्दांत व मुद्देसूद स्वरूपात तयार करण्यात आला आहे.
प्रस्तावना
पाणी (Water) हे पृथ्वीवरील सर्वात महत्त्वाचे नैसर्गिक संसाधन (Natural Resource) आहे. Life on Earth is impossible without water. मानव, प्राणी, वनस्पती, शेती, उद्योग, ऊर्जा निर्मिती आणि पर्यावरण संतुलन या सर्वांसाठी पाणी अत्यावश्यक आहे. Geography विषयामध्ये Water हा घटक CTET-2026 साठी खूप महत्त्वाचा असून, तो Natural Resources, Hydrological Cycle, Water Distribution, Uses of Water, Water Scarcity, Conservation of Water अशा अनेक घटकांशी संबंधित आहे.
CTET-2026 – Natural Resources (Geography)
Ministry of Jal Shakti – Government of India
1. पाण्याचे महत्त्व
Water is called the “Elixir of Life”. पाण्याशिवाय पृथ्वीवर जीवन शक्य नाही.
पाण्याचे महत्त्व:
- Drinking water for humans and animals
- Agriculture (Irrigation)
- Industries and power generation
- Transportation (Rivers, seas)
- Climate regulation
- Ecosystem balance
मानव शरीरात सुमारे 70% पाणी असते. त्यामुळे पाण्याचे महत्त्व CTET च्या दृष्टीने खूप मूलभूत आहे.
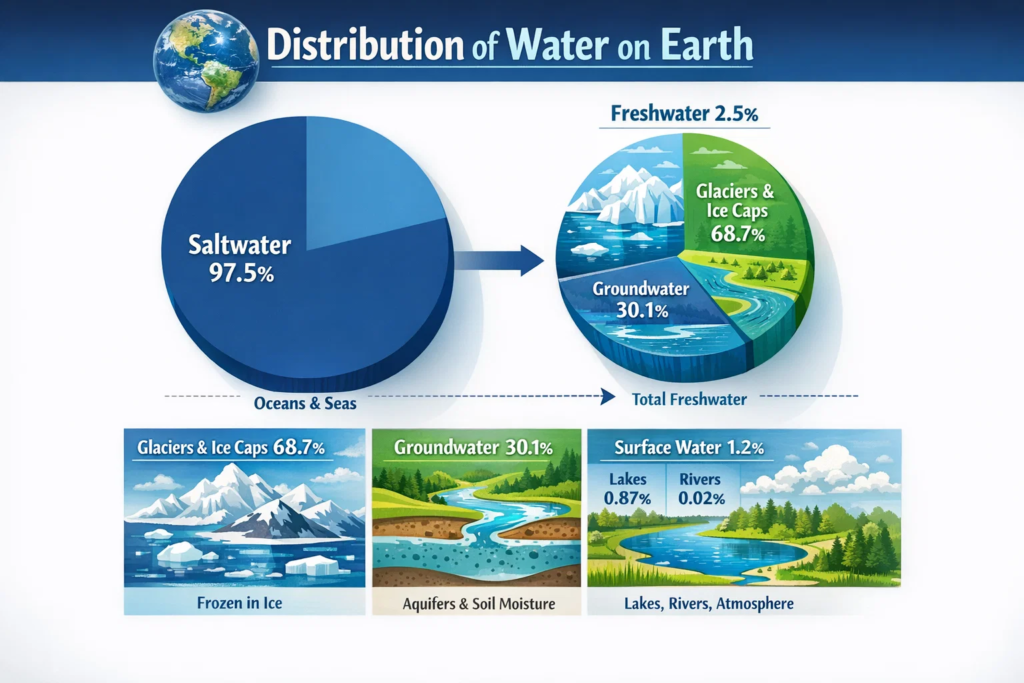
2. पृथ्वीवरील पाण्याचे वितरण
Earth is known as the “Blue Planet” because about 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered with water.
पाण्याचे प्रकार:
- Salt Water (खारट पाणी) – सुमारे 97%
- Seas and Oceans
- Fresh Water (गोडे पाणी) – फक्त 3%
Fresh water चे वितरण:
- Glaciers & Ice Caps – 69%
- Groundwater – 30%
- Rivers, Lakes & Ponds – Less than 1%
👉 यावरून गोड्या पाण्याची उपलब्धता फारच मर्यादित आहे हे स्पष्ट होते.
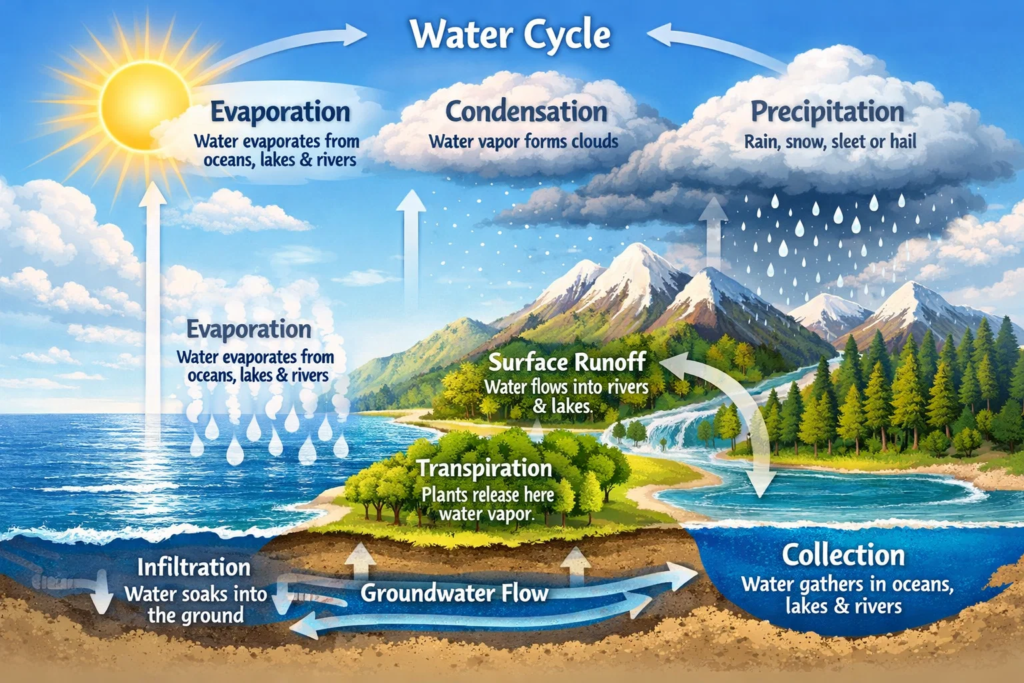
3. जलचक्र (Hydrological Cycle )
Water on Earth moves continuously through a natural process called the Hydrological Cycle .
जलचक्राचे टप्पे:
- Evaporation (बाष्पीभवन)
सूर्याच्या उष्णतेमुळे पाणी वाफेत रूपांतरित होते. - Condensation (संघनन)
वाफ थंड होऊन ढग तयार होतात. - Precipitation (पर्जन्य)
Rain, snow, hail या स्वरूपात पाणी पृथ्वीवर पडते. - Runoff & Infiltration
- Runoff – पाणी नद्यांमध्ये वाहते
- Infiltration – पाणी जमिनीत मुरते
CTET मध्ये जलचक्रावर conceptual MCQs विचारले जातात.
4. पाण्याचे स्रोत
(A) Surface Water (पृष्ठीय पाणी)
- Rivers (नद्या)
- Lakes (तलाव)
- Ponds (तळी)
- Reservoirs (धरणे)
(B) Groundwater (भूजल)
- Wells (विहिरी)
- Tube wells
- Springs
(C) Atmospheric Water
- Rainfall
- Snowfall
5. नद्या आणि त्यांचे महत्त्व
Rivers are the lifelines of human civilization.
नद्यांचे महत्त्व:
- Irrigation
- Drinking water
- Hydroelectric power
- Transportation
- Fertile plains formation
भारतामधील प्रमुख नद्या:
- Ganga, Yamuna
- Godavari, Krishna
- Narmada, Tapi
- Brahmaputra
CTET मध्ये river-based questions वारंवार विचारले जातात.
6. पाण्याचे उपयोग
(1) Domestic Use:
- Drinking
- Cooking
- Washing
- Sanitation
(2) Agricultural Use:
- Irrigation
- Livestock farming
(3) Industrial Use:
- Manufacturing
- Cooling
- Processing
(4) Energy Production:
- Hydroelectric power
7. पाणीटंचाई
Water Scarcity means lack of sufficient available water resources.
पाणीटंचाईची कारणे:
- Population growth
- Overuse of groundwater
- Pollution of water sources
- Climate change
- Unequal distribution
India is facing severe water stress in many regions.
8. पाण्याचे प्रदूषण
Water Pollution occurs when harmful substances enter water bodies.
Sources of Water Pollution:
- Industrial waste
- Domestic sewage
- Agricultural chemicals
- Plastic waste
परिणाम:
- Harm to aquatic life
- Spread of diseases
- Unsafe drinking water
9. पाणी संवर्धन
Water conservation is the need of the hour.
पाणी संवर्धनाच्या पद्धती:
- Rainwater harvesting
- Drip irrigation
- Recycling of water
- Preventing leakage
- Afforestation
Rainwater Harvesting:
Rainwater is collected and stored for future use.
It helps in recharging groundwater.
10. भारतातील जल व्यवस्थापन
Major initiatives:
- Jal Jeevan Mission
- Atal Bhujal Yojana
- National Water Policy
Objectives:
- Safe drinking water
- Sustainable use of water
- Conservation of water resources
11. शिक्षणात पाण्याचे महत्त्व – (CTET Perspective)
As a teacher, it is important to:
- Create awareness about water conservation
- Teach students about water cycle
- Encourage eco-friendly habits
- Use activity-based learning
CTET मध्ये Environmental Studies (EVS) आणि Geography मध्ये हा विषय खूप महत्त्वाचा आहे.
12. CTET Exam Point of View (
- Water cycle diagram based questions
- Fresh water vs salt water
- Causes of water scarcity
- Conservation methods
- Importance of rivers
CTET-2026 – Geography| 50 MCQs
1. Earth ला “Blue Planet” का म्हणतात?
A) Forests जास्त आहेत
B) Land जास्त आहे
C) Water जास्त आहे
D) Mountains जास्त आहेत
Ans: C
2. पृथ्वीच्या पृष्ठभागावर सुमारे किती टक्के भाग पाण्याने व्यापलेला आहे?
A) 51%
B) 61%
C) 71%
D) 81%
Ans: C
3. पृथ्वीवरील एकूण पाण्यापैकी किती टक्के पाणी खारट आहे?
A) 3%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 97%
Ans: D
4. Fresh water चे सर्वाधिक प्रमाण कुठे आढळते?
A) Rivers
B) Lakes
C) Groundwater
D) Glaciers & Ice caps
Ans: D
5. जलचक्रातील पहिली प्रक्रिया कोणती?
A) Condensation
B) Precipitation
C) Evaporation
D) Infiltration
Ans: C
6. Evaporation म्हणजे काय?
A) पाणी थंड होणे
B) पाणी वाफेत रूपांतर होणे
C) पावसाचे पडणे
D) पाणी जमिनीत मुरणे
Ans: B
7. ढग तयार होण्याची प्रक्रिया कोणती?
A) Evaporation
B) Precipitation
C) Condensation
D) Runoff
Ans: C
8. Rain, snow, hail या प्रक्रियेला काय म्हणतात?
A) Evaporation
B) Condensation
C) Precipitation
D) Transpiration
Ans: C
9. Runoff म्हणजे काय?
A) पाणी बाष्परूप होणे
B) पाणी जमिनीत मुरणे
C) पाणी नद्यांमधून वाहणे
D) पाणी गोठणे
Ans: C
10. भूजल (Groundwater) कसा साठतो?
A) Evaporation मुळे
B) Infiltration मुळे
C) Condensation मुळे
D) Transpiration मुळे
Ans: B
11. खालीलपैकी पृष्ठीय पाण्याचा स्रोत कोणता?
A) Well
B) Tube well
C) River
D) Spring
Ans: C
12. नद्या मानव सभ्यतेसाठी महत्त्वाच्या का आहेत?
A) Transportation
B) Irrigation
C) Fertile soil
D) All of the above
Ans: D
13. ‘भारताची जीवनरेखा’ कोणती नदी मानली जाते?
A) Yamuna
B) Ganga
C) Godavari
D) Krishna
Ans: B
14. Hydroelectric power कोणत्या स्रोतावर आधारित आहे?
A) Wind
B) Solar
C) Water
D) Coal
Ans: C
15. पाण्याचा सर्वाधिक वापर कोणत्या क्षेत्रात होतो?
A) Domestic
B) Industrial
C) Agriculture
D) Transport
Ans: C
16. Water scarcity म्हणजे काय?
A) पाणी जास्त असणे
B) पाणी प्रदूषित असणे
C) पाण्याची कमतरता
D) पाणी साठवण
Ans: C
17. पाणीटंचाईचे मुख्य कारण कोणते?
A) Population growth
B) Water pollution
C) Overuse of groundwater
D) All of the above
Ans: D
18. खालीलपैकी कोणते पाण्याचे प्रदूषण करते?
A) Industrial waste
B) Sewage
C) Agricultural chemicals
D) All of the above
Ans: D
19. पाण्याचे प्रदूषणाचा परिणाम कोणता?
A) Diseases
B) Aquatic life damage
C) Unsafe drinking water
D) All of the above
Ans: D
20. Water conservation म्हणजे काय?
A) पाण्याचा अपव्यय
B) पाण्याचा योग्य वापर
C) पाणी प्रदूषण
D) पाणी नष्ट करणे
Ans: B
21. Rainwater harvesting म्हणजे काय?
A) पावसाचे पाणी वाया घालवणे
B) पावसाचे पाणी साठवणे
C) नदीचे पाणी वापरणे
D) समुद्राचे पाणी वापरणे
Ans: B
22. Rainwater harvesting चा फायदा कोणता?
A) Groundwater recharge
B) Flood control
C) Water availability
D) All of the above
Ans: D
23. Drip irrigation चा मुख्य फायदा कोणता?
A) Water wastage
B) Less crop yield
C) Efficient water use
D) Soil erosion
Ans: C
24. Jal Jeevan Mission चा उद्देश काय आहे?
A) Electricity supply
B) Safe drinking water
C) Road construction
D) Education
Ans: B
25. भारतातील जल व्यवस्थापनासाठी कोणती योजना आहे?
A) PM Awas Yojana
B) Atal Bhujal Yojana
C) MNREGA
D) PM Fasal Bima
Ans: B
26. Groundwater चा अति वापर केल्यास काय होते?
A) Water table rises
B) Water table falls
C) Rainfall increases
D) Floods
Ans: B
27. कोणता घटक जलचक्राचा भाग नाही?
A) Evaporation
B) Condensation
C) Precipitation
D) Photosynthesis
Ans: D
28. Transpiration ही प्रक्रिया कोणाशी संबंधित आहे?
A) Animals
B) Plants
C) Rivers
D) Oceans
Ans: B
29. Fresh water चा सर्वात कमी साठा कुठे आहे?
A) Rivers
B) Lakes
C) Glaciers
D) Oceans
Ans: A
30. भारतात सर्वाधिक लांबीची नदी कोणती?
A) Yamuna
B) Godavari
C) Ganga
D) Narmada
Ans: C
31. पाणी संवर्धन का आवश्यक आहे?
A) Limited freshwater
B) Population growth
C) Climate change
D) All of the above
Ans: D
32. Climate change चा परिणाम पाण्यावर कसा होतो?
A) Rainfall pattern बदलते
B) Drought वाढतो
C) Floods वाढतात
D) All of the above
Ans: D
33. नदीमुखाजवळ तयार होणाऱ्या भूमीला काय म्हणतात?
A) Plateau
B) Delta
C) Valley
D) Gorge
Ans: B
34. समुद्रातील पाणी खारट का असते?
A) High evaporation
B) Dissolved salts
C) Rainfall
D) Rivers
Ans: B
35. पाण्याचा पुनर्वापर म्हणजे काय?
A) Water wastage
B) Water recycling
C) Water pollution
D) Water loss
Ans: B
36. Waterborne diseases कोणत्या माध्यमातून पसरतात?
A) Air
B) Food
C) Contaminated water
D) Soil
Ans: C
37. पाणी हे कोणत्या प्रकारचे संसाधन आहे?
A) Renewable
B) Non-renewable
C) Human-made
D) Mineral
Ans: A
38. नदीच्या उगमाजवळ भूभाग कसा असतो?
A) Flat
B) Steep
C) Desert
D) Delta
Ans: B
39. Floods होण्याचे एक कारण कोणते?
A) Excess rainfall
B) Deforestation
C) Poor drainage
D) All of the above
Ans: D
40. EVS मध्ये Water topic का महत्त्वाचा आहे?
A) Environmental awareness
B) Sustainable development
C) Life skills
D) All of the above
Ans: D
41. जलसंधारण म्हणजे काय?
A) Water storage
B) Water wastage
C) Water pollution
D) Water loss
Ans: A
42. Aquatic life म्हणजे काय?
A) Land animals
B) Air animals
C) Water organisms
D) Forest animals
Ans: C
43. पाण्याचा सर्वात शुद्ध नैसर्गिक स्रोत कोणता?
A) River
B) Lake
C) Rainwater
D) Sea
Ans: C
44. Dam बांधण्याचा उद्देश कोणता?
A) Irrigation
B) Power generation
C) Flood control
D) All of the above
Ans: D
45. पाणी प्रदूषण कमी करण्यासाठी काय करावे?
A) Waste treatment
B) Plastic reduction
C) Public awareness
D) All of the above
Ans: D
46. जलचक्रामुळे काय होते?
A) Water balance maintained
B) Climate regulation
C) Life sustainability
D) All of the above
Ans: D
47. Water table म्हणजे काय?
A) Sea level
B) Groundwater level
C) River depth
D) Rainfall level
Ans: B
48. Which sector consumes maximum freshwater globally?
A) Industry
B) Domestic
C) Agriculture
D) Transport
Ans: C
49. भारतातील पाण्याची समस्या मुख्यतः कशामुळे आहे?
A) Unequal distribution
B) Population pressure
C) Pollution
D) All of the above
Ans: D
50. “Save Water, Save Life” या घोषणेचा अर्थ काय?
A) पाणी साठवा
B) पाणी वाया घालवा
C) पाण्याचे महत्त्व ओळखा
D) A and C both
Ans: D
निष्कर्ष
Water is a precious natural resource. “Save Water, Save Life” हे केवळ वाक्य नसून एक जबाबदारी आहे. वाढती लोकसंख्या, प्रदूषण आणि हवामान बदलामुळे पाण्याची समस्या गंभीर होत आहे. त्यामुळे water conservation, sustainable use and awareness are essential. CTET-2026 साठी Water (Geography) हा विषय conceptual clarity, diagrams आणि real-life examples सह अभ्यासणे अत्यंत आवश्यक आहे.

